What Buyers Look for in Biostimulant Raw Materials
When sourcing biostimulant raw materials, buyers increasingly prioritize ingredients that deliver measurable crop performance while meeting evolving regulatory and sustainability requirements. Modern procurement teams expect raw materials to be biologically active, stable under diverse storage and application conditions, and compatible with existing fertilization and irrigation systems. Reliability, shelf stability, environmental compatibility, and proven effects on nutrient efficiency and stress tolerance are now core expectations across global markets.
As biostimulants gain importance in sustainable agriculture, procurement decisions are no longer driven by cost alone. Instead, buyers assess raw materials based on their technical performance, consistency, regulatory compliance, and long-term supply security. This article outlines the key criteria buyers use to evaluate biostimulant raw materials and reminders to consider when selecting inputs for competitive agricultural formulations.

Understanding Biostimulant Raw Materials
Biostimulant raw materials include a wide range of natural and processed substances that enhance plant growth, nutrient uptake, and stress resilience without acting as conventional fertilizers. Rather than supplying nutrients directly, biostimulants support plant physiological processes, helping crops make more efficient use of available resources.
The Role of Biostimulants in Modern Agriculture
Biostimulants support plant metabolism, root development, microbial activity, and photosynthetic efficiency. Their use is expanding as growers face increasing pressure from climate variability, soil degradation, and regulatory limits on chemical fertilizer inputs. Industry data indicates that the global biostimulant market has experienced sustained double-digit annual growth, reflecting strong adoption across both conventional and sustainable farming systems.
Major Categories of Biostimulant Raw Materials
Amino acids and protein hydrolysates remain among the most widely used biostimulant inputs. These materials contribute to enzyme formation, protein synthesis, and stress recovery, with rapid plant uptake—particularly when derived from high-quality protein sources such as yeast.
Humic and fulvic acids, derived from decomposed organic matter, are valued for their effects on soil structure, nutrient chelation, and microbial activity. Their complex molecular structures allow them to interact with minerals and organic compounds, making them useful in soil-applied and fertigation formulations.
Seaweed extracts provide a broad spectrum of bioactive compounds, including natural growth regulators, trace elements, and polysaccharides. Their effectiveness depends strongly on raw material origin and extraction technology, which influence both bioactivity and product stability.
Bioactive Compounds and Functional Mechanisms
Advanced biostimulant raw materials increasingly focus on defined bioactive components. Microbial inputs such as beneficial fungi and plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) improve nutrient availability and plant resilience but require careful handling to maintain viability.
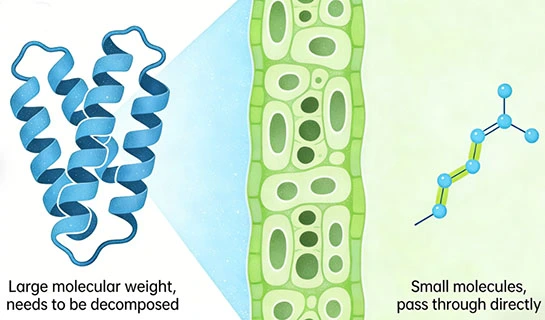
Peptides with low molecular weight have gained attention due to their high bioavailability and stability. Materials with molecular weights below 1000 Daltons are often associated with faster uptake and consistent performance across environmental conditions. Controlled enzymatic processing enables the production of peptide profiles with predictable biological activity.
Core Evaluation Criteria for Biostimulant Buyers
Professional buyers apply structured evaluation frameworks to ensure that biostimulant raw materials meet both performance and compliance expectations. These criteria influence formulation success, regulatory approval, and market acceptance.
Quality, Purity, and Consistency
Purity is a primary concern for biostimulant raw materials. Contaminants such as heavy metals, residual solvents, or unwanted by-products can affect product safety and regulatory compliance. Reputable suppliers provide detailed certificates of analysis covering protein content, molecular weight distribution, and impurity limits.
Batch-to-batch consistency is equally critical. Stable production processes and robust quality control systems help ensure predictable formulation behavior and consistent field results. Buyers often assess supplier capabilities through incoming material testing, production audits, and long-term performance data.
Regulatory Compliance and Traceability
Biostimulant raw materials must comply with regional regulations governing agricultural inputs. Certifications such as ISO standards, organic approvals, and relevant market-specific registrations reduce regulatory risk and support international commercialization.
Traceability documentation has become increasingly important as regulatory oversight intensifies. Buyers favor suppliers who can demonstrate transparent sourcing, controlled processing, and comprehensive quality records, particularly when targeting high-value or organic markets.
Stability and Compatibility
Shelf stability and thermal tolerance are essential performance indicators, especially for products distributed globally or stored under variable climatic conditions. Raw materials that retain bioactivity across temperature ranges simplify logistics and improve customer confidence.
Compatibility with fertilizers, crop protection products, and irrigation systems is also critical. Materials with stable pH behavior and minimal interaction risks allow greater formulation flexibility and ease of application for end users.
Selecting Raw Materials for Different Crops and Applications
Choosing appropriate biostimulant raw materials requires aligning material properties with crop type, application method, and market positioning. Different agricultural systems place different demands on input performance.
Natural Versus Processed Material Options
Natural raw materials are often preferred in organic and sustainability-focused markets due to regulatory acceptance and environmental perception. However, natural inputs may show greater variability depending on source material and processing conditions.
Processed or engineered materials, including defined peptides and amino acid blends, offer higher consistency and formulation control. These options are often favored in large-scale production where reproducibility and cost efficiency are critical. The choice depends on target markets, regulatory frameworks, and product differentiation strategies.
Crop-Specific Performance Considerations
Fruit crops such as citrus, grapes, and stone fruits often benefit from biostimulants that enhance stress tolerance and fruit quality. Cereals may require materials that support root development and nutrient efficiency during early growth stages.
Vegetable production systems, particularly for high-value crops, prioritize uniform growth, yield stability, and nutritional quality. Leafy vegetables often respond well to inputs that promote rapid biomass accumulation and efficient nitrogen metabolism.
Physical Form and Processing Factors
Liquid and powder forms present different advantages. Liquids are generally easier to blend and apply but may have shorter shelf lives. Powders offer improved storage stability and reduced transport costs but require effective dispersion during formulation.
Particle size, solubility, and dissolution rate influence both processing efficiency and bioavailability. These physical characteristics should align with intended application methods and production capabilities.

Procurement Strategy and Supply Chain Considerations
Beyond technical performance, procurement teams evaluate suppliers based on reliability, scalability, and long-term partnership potential.
Supplier Qualification and Technical Support
Supplier assessments typically include reviews of manufacturing capacity, R&D investment, and quality management systems. Suppliers with proprietary processing technologies and strong technical support capabilities can add value beyond basic material supply.
Production scale and geographic location affect supply security, logistics costs, and responsiveness to market demand. Large-capacity producers often provide greater pricing stability and delivery reliability.
Cost Management and Risk Mitigation
Bulk purchasing and long-term contracts can improve cost efficiency but require careful demand forecasting and inventory management. Buyers increasingly seek flexible pricing structures and transparent communication to manage currency and trade-related risks.
Diversifying supply sources reduces dependency on single suppliers and improves resilience against disruptions. However, maintaining consistent quality across multiple suppliers requires rigorous qualification and monitoring systems.
Long-Term Market Alignment
Effective procurement strategies consider how raw material choices influence product differentiation, regulatory positioning, and customer trust. Regular supplier audits, performance reviews, and technical collaboration support continuous improvement and innovation.
Conclusion
Selecting biostimulant raw materials is a strategic decision that directly influences product performance, regulatory compliance, and long-term market success. Buyers must evaluate purity, stability, traceability, and supplier capability alongside cost considerations. As the biostimulant industry continues to evolve, advances in processing technology and increasing demand for sustainable solutions will further raise expectations for raw material quality and consistency.
By applying structured evaluation criteria and maintaining strong supplier partnerships, procurement teams can secure raw materials that support reliable formulations and competitive positioning in modern agriculture.

FAQ
Q1: What are the most important quality parameters for biostimulant raw materials?
Key parameters include protein content, molecular weight distribution, purity, and bioactivity. High-quality materials typically contain ≥60% protein, optimized for bioavailability, and must pass heavy metal, contaminant, and microbiological safety tests to ensure regulatory compliance.
Q2: How can buyers evaluate supplier reliability?
Buyers should assess production capacity, processing technology, quality control systems, and regulatory compliance. Suppliers with scalable manufacturing, consistent batch quality, and strong technical support offer greater long-term reliability.
Q3: What advantages do yeast-derived materials offer?
Yeast-derived materials provide consistent composition, high bioavailability, and strong thermal stability. As an alternative to plant and animal proteins, they offer reliable performance and good compatibility across a wide range of agricultural formulations.
Partner with LYS for Premium Biostimulant Raw Materials
LYS delivers exceptional biostimulant raw materials that meet the demanding requirements of modern agricultural applications. Our proprietary FSDT technology and 70+ years of expertise ensure consistent quality and superior performance for your formulation needs. With 10,000 MT annual production capacity and comprehensive technical support, we provide a reliable partnership for manufacturers and distributors seeking premium materials. Contact alice@aminoacidfertilizer.com to discuss your biostimulant supplier requirements and discover how our yeast-derived peptides can enhance your product portfolio.
References
1. Martinez-Garcia, S., & Thompson, R. (2023). "Advanced Processing Technologies for Biostimulant Raw Materials: A Comprehensive Review." Journal of Agricultural Technology Innovation, 18(3), 245-267.
2. Chen, L., Rodriguez, M., & Williams, K. (2024). "Quality Assessment Protocols for Commercial Biostimulant Raw Materials." International Agriculture Quality Standards Review, 12(1), 89-112.
3. Anderson, P., Kumar, S., & Lee, H. (2023). "Enzymatic Hydrolysis Systems in Biostimulant Production: Optimization and Scale-up Considerations." Biotechnology in Agriculture Quarterly, 29(4), 156-178.
4. Johnson, D., & Park, Y. (2024). "Supply Chain Management Strategies for Global Biostimulant Raw Material Procurement." Agricultural Supply Chain Management Journal, 15(2), 78-95.
5. Wilson, A., Garcia, F., & Zhang, Q. (2023). "Regulatory Compliance and Certification Requirements for International Biostimulant Raw Materials." Global Agricultural Regulations Review, 8(3), 201-223.
6. Brown, M., Singh, R., & O'Connor, J. (2024). "Emerging Trends in Biostimulant Raw Material Innovation: Market Analysis and Future Projections." Agricultural Innovation Trends Quarterly, 11(1), 134-152.

Tell us your needs — we’ll provide the right solution for your crops and markets.

Innovating Agriculture with Yeast-Derived Amino Acid Peptides


