The Science Behind Biostimulants: From Soil Health to Crop Resilience
Biostimulants represent an emerging frontier in agricultural science, offering a sustainable approach to enhancing crop productivity and resilience. These natural substances and microorganisms work harmoniously with plants to optimize nutrient uptake, improve stress tolerance, and strengthen overall plant health. Unlike conventional fertilizers or pesticides, biostimulants function by stimulating natural physiological processes in plants and the soil ecosystem.
As global agriculture faces increasing challenges—including climate variability, soil degradation, and the need for sustainable production—biostimulants have gained significant attention. Their scientific foundation is multifaceted, involving complex interactions among plants, soil microorganisms, and environmental factors. Biostimulants typically include humic substances, seaweed extracts, microbial inoculants, and protein hydrolysates, each acting through unique mechanisms to support crop growth and development.
This article explores the science behind biostimulants, detailing how they enhance soil health, improve root architecture, support nutrient uptake, and contribute to long-term sustainability in modern agriculture.

How Biostimulants Enhance Soil Microbial Activity?
The soil microbiome plays a vital role in plant productivity and long-term soil fertility. Biostimulants have emerged as effective tools to enhance soil microbial activity, creating a more dynamic and supportive environment for plant growth. This improvement occurs through several interconnected mechanisms.
Promoting Beneficial Microorganism Populations
Certain biostimulants—especially those containing microbial inoculants or natural organic compounds—help introduce or stimulate populations of beneficial soil microorganisms. These include species such as Bacillus, Pseudomonas, and mycorrhizal fungi. By forming symbiotic relationships with plant roots, these microbes enhance nutrient uptake efficiency and support natural pathogen suppression.
Stimulating Microbial Metabolic Activity
Biostimulants containing amino acids or protein hydrolysates provide easily accessible carbon and nitrogen sources for soil microbes. These inputs accelerate microbial metabolism, improving nutrient cycling and soil structure.
Enhancing Soil Enzyme Activities
Many biostimulants are formulated to increase the activity of soil enzymes, which are essential for breaking down organic matter and releasing nutrients in plant-available forms. Enhanced enzyme activity improves nutrient availability and supports long-term soil fertility.
Collectively, these improvements in microbial activity result in better soil structure, higher organic matter content, and improved water-holding capacity—creating a more resilient soil environment capable of supporting crops under various environmental stresses.
Improvement in Root Architecture and Nutrient Uptake
One of the most significant effects of biostimulants is their ability to enhance root architecture and increase nutrient uptake efficiency—especially important in low-fertility soils or under environmental stress.
Stimulating Root Growth and Development
Biostimulants containing compounds such as peptides, auxin-like molecules, or cytokinins can directly stimulate root growth. They promote lateral root formation and root hair development, greatly increasing the root surface area and improving the plant’s ability to explore the soil profile for water and nutrients.
Enhancing Nutrient Transport Systems
Seaweed extracts and similar biostimulants have been shown to upregulate genes involved in nutrient transport, including nitrate and phosphate transporters. This enhances nutrient absorption from the soil.
Improving Nutrient Solubility and Availability
Humic substances within biostimulants can chelate micronutrients, making them more soluble and available to plants. Additionally, certain biostimulants can modify rhizosphere pH, improving the solubility of key nutrients.
By enhancing both root development and internal nutrient transport processes, biostimulants improve nutrient use efficiency—a key objective for sustainable farming systems aiming to reduce environmental impact while maintaining high yields.

Long‑term Benefits for Sustainable Farming
The advantages of biostimulants extend far beyond immediate yield improvements. Their long-term benefits align strongly with the principles of sustainable agriculture.
Soil Health Improvement
Continuous use of biostimulants can increase microbial diversity and organic matter content, improve soil structure, and enhance water retention. These improvements strengthen soil resilience and long-term productivity.
Reduced Chemical Inputs
Because biostimulants enhance nutrient uptake efficiency and support natural plant defense processes, they can reduce the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides. This not only lowers production costs but also minimizes environmental impact.
Climate Change Resilience
Biostimulants help plants better withstand drought, salinity, temperature extremes, and other climate-related stresses by activating natural defense pathways. This resilience supports more stable yields under unpredictable weather conditions.
Biodiversity Promotion
By encouraging a diverse soil ecosystem, biostimulants indirectly support above-ground biodiversity as well. Healthy ecosystems contribute to natural pest regulation and pollination, reducing the dependence on chemical interventions.Overall, biostimulants contribute to ecological, economic, and social sustainability, making them a valuable component of modern agricultural strategies.
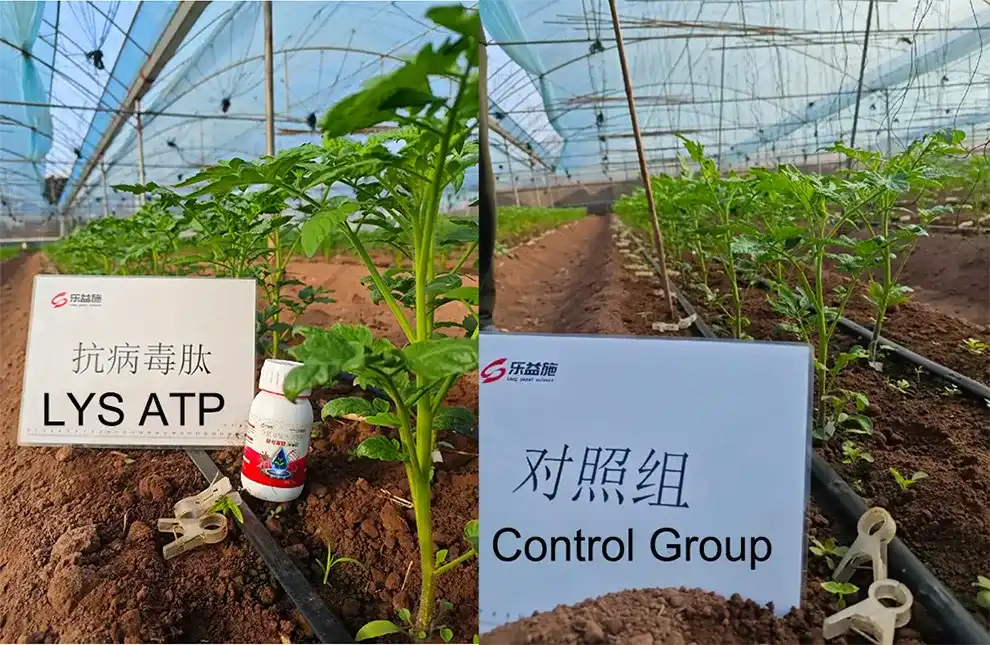

Conclusion
The science behind biostimulants reveals their significant potential in transforming agricultural practices. From enhancing soil microbial activity to improving root architecture and nutrient uptake, biostimulants offer a holistic approach to crop management that aligns closely with sustainable farming principles. Their long-term benefits—such as improved soil health, reduced chemical inputs, and enhanced climate resilience—position them as essential tools for addressing today’s agricultural challenges.
For agricultural professionals seeking reliable and innovative biostimulant solutions, partnering with a trusted supplier is essential. Shenzhen LYS Biotech, with more than 70 years of expertise in yeast-enzyme fermentation technology, offers advanced biostimulant products designed to meet diverse agricultural needs. Our proprietary fermentation processes, high-quality raw materials, and rigorous quality control ensure consistent and high-performance results.
Whether you are an agrochemical manufacturer enhancing product formulations, a large-scale distributor seeking differentiated high-value products, or a farming operation aiming to improve crop resilience and yield, LYS Biotech provides the expertise and products to support your goals. Our commitment to innovation and sustainable agricultural development aligns perfectly with the growing global demand for effective and environmentally responsible crop inputs.
Take the next step toward optimizing your agricultural operations with science-backed biostimulant solutions. Contact LYS Biotech today to explore how our advanced biostimulant technologies can support your business and contribute to a more sustainable agricultural future.

FAQs
Q1: What makes LYS ECO's biostimulants unique in the market?
A: LYS ECO's biostimulants stand out due to our exclusive centre-licensed fixing, "nucleotide," which upgrades safe reaction and advances cell division. Our items also highlight a high concentration of small atom peptides, guaranteeing fast retention and adequacy. This one-of-a-kind combination, supported by over 70 a long time of experience in yeast protein innovation, comes about in biostimulants that exceed expectations in advancing trim development, improving resistance, and enhancing yield and quality.
Q2: How do LYS ECO's biostimulants contribute to sustainable farming practices?
A: Our biostimulants contribute to feasible cultivation by upgrading soil health, making strides in supplement uptake effectiveness, and expanding edit versatility to environmental stresses. This leads to decreased requirement for chemical inputs, improved water utilize effectiveness, and superior by and large edit execution. By utilising our items, ranchers can accomplish higher yields while minimising environmental impact, aligning with long-term sustainability goals.
Q3: Can LYS ECO's biostimulants be integrated into existing agricultural systems?
A: Completely. LYS ECO's biostimulants are planned to complement existing rural homes and can be effortlessly coordinated into different edit administration frameworks. Whether you're practising ordinary, natural, or exactness horticulture, our items can be consolidated to improve the overall framework execution. We offer specialised back to guarantee ideal integration and comes about for your particular rural context.
Innovative Biostimulants for Enhanced Crop Performance | LYS
Ready to revolutionise your agricultural practices with cutting-edge biostimulant solutions? LYS ECO offers a range of innovative, high-performance biostimulants designed to enhance soil health, improve crop resilience, and boost yields sustainably. Our products are backed by rigorous scientific research and over seven decades of expertise in yeast enzyme technology. Whether you're a manufacturer looking to enhance your product line, a distributor seeking premium agricultural inputs, or a large-scale farmer aiming to optimise crop performance, we have the solutions to meet your needs. Don't miss out on the opportunity to transform your agricultural operations. Contact us today at alice@aminoacidfertilizer.com to learn more about our biostimulant products and how they can benefit your business. Let's work together towards a more productive and sustainable agricultural future.
References
1. Du Jardin, P. (2015). Plant biostimulants: Definition, concept, main categories and regulation. Scientia Horticulturae, 196, 3-14.
2. Calvo, P., Nelson, L., & Kloepper, J. W. (2014). Agricultural uses of plant biostimulants. Plant and Soil, 383(1), 3-41.
3. Rouphael, Y., & Colla, G. (2018). Synergistic biostimulatory action: Designing the next generation of plant biostimulants for sustainable agriculture. Frontiers in Plant Science, 9, 1655.
4. Van Oosten, M. J., Pepe, O., De Pascale, S., Silletti, S., & Maggio, A. (2017). The role of biostimulants and bioeffectors as alleviators of abiotic stress in crop plants. Chemical and Biological Technologies in Agriculture, 4(1), 5.
5. Yakhin, O. I., Lubyanov, A. A., Yakhin, I. A., & Brown, P. H. (2017). Biostimulants in plant science: A global perspective. Frontiers in Plant Science, 7, 2049.
6. Povero, G., Mejia, J. F., Di Tommaso, D., Piaggesi, A., & Warrior, P. (2016). A systematic approach to discover and characterize natural plant biostimulants. Frontiers in Plant Science, 7, 435.

Tell us your needs — we’ll provide the right solution for your crops and markets.

Innovating Agriculture with Yeast-Derived Amino Acid Peptides


