From Nutrition to Signal: Upgrading Liquid Fertilizers with Small Peptides
Modern agriculture faces unprecedented challenges as producers seek sustainable ways to increase yields while preserving long-term soil health. Conventional liquid fertilizer systems are effective at supplying basic nutrients, but they often fall short in addressing the complex physiological demands of crops under stress. Recent advances in agricultural science have introduced small peptides into liquid fertilizer formulations, marking a shift from simple nutrient delivery toward signal-based plant management.
These bioactive peptides function as molecular messengers that influence nutrient uptake, metabolic efficiency, and plant defense mechanisms. For purchasing managers, agricultural engineers, and input distributors, peptide-enhanced liquid fertilizer solutions represent a next-generation category of agricultural inputs designed to improve crop performance, stress tolerance, and yield quality across diverse production environments.

Liquid Fertilizer Fundamentals and the Emergence of Peptide Technology
Core Functions of Liquid Fertilizer Systems
Liquid fertilizer products traditionally provide essential macronutrients—nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium—along with key micronutrients such as iron, zinc, and manganese. Delivered through fertigation, foliar spraying, or irrigation systems, liquid fertilizer allows precise dosing and rapid nutrient availability compared with granular alternatives.
This fast nutrient accessibility makes liquid fertilizer particularly valuable during critical growth stages when crops require immediate nutritional support. However, while effective for baseline nutrition, conventional liquid fertilizer formulations primarily address nutrient supply rather than plant physiological regulation.
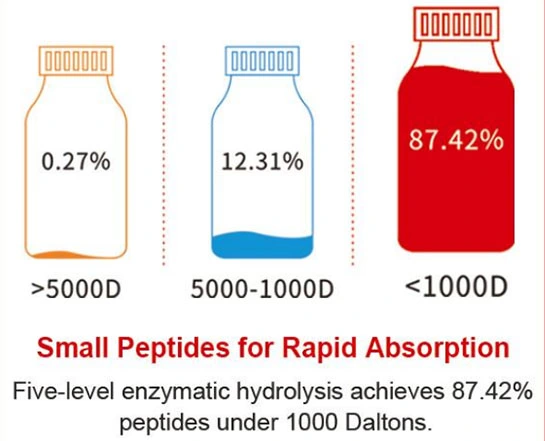
Why Small Peptides Matter in Plant Nutrition
Small peptides consist of short chains of amino acids, typically with molecular weights below 1000 Daltons. This low molecular weight enables efficient absorption by plant tissues and facilitates their role as bioactive signaling compounds. Within plant systems, these peptides participate in regulatory processes that influence gene expression, enzyme activity, and metabolic pathway coordination.
When integrated into liquid fertilizer formulations, small peptides act not only as organic nutrient sources but also as biological activators, enhancing how plants perceive and respond to their growing environment.
Molecular Weight Advantages in Agricultural Applications
The compact molecular structure of small peptides allows plants to absorb them with minimal energy expenditure. This advantage becomes particularly important under stress conditions, when plant metabolic resources are limited. Research indicates that peptides below 1000 Da maintain functional stability across variable temperatures, enabling consistent performance under fluctuating climatic conditions.
These characteristics make peptide-enhanced liquid fertilizer systems suitable for both open-field agriculture and controlled-environment production.
From Nutrient Supply to Signal-Based Crop Management
Limitations of Conventional Liquid Fertilizer Under Stress
Under adverse conditions such as drought, salinity, temperature extremes, or nutrient imbalance, plants often exhibit reduced nutrient uptake efficiency. Even when nutrients are readily available through liquid fertilizer applications, physiological stress can limit their effective utilization, leading to nutrient loss, increased application frequency, and inconsistent crop performance.
These limitations increase production costs, contribute to environmental nutrient loss, and reduce overall farm profitability.
Peptide Integration as a Functional Upgrade
Incorporating small peptides into liquid fertilizer formulations addresses these challenges by enhancing the plant’s intrinsic nutrient uptake and utilization mechanisms. Peptide-enhanced liquid fertilizer products have demonstrated improved nutrient efficiency, reduced application requirements, and stronger physiological resilience under stress conditions.
This approach is particularly effective in high-precision systems such as hydroponics and fertigation-based agriculture, where nutrient management directly influences yield outcomes.
Field Performance and Commercial Case Data
Commercial trials across multiple crop categories have reported measurable benefits from peptide-enhanced liquid fertilizer programs. Tomato production systems have recorded yield increases of 15–20%, accompanied by improved fruit sugar content and extended shelf life. Leafy green producers report shorter growth cycles and improved tolerance to heat and water stress.
These performance gains translate into tangible economic advantages, including reduced input costs, improved market quality premiums, and enhanced operational efficiency.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Improved Nutrient Efficiency and Reduced Losses
By increasing nutrient uptake efficiency, peptide-enhanced liquid fertilizer systems reduce nutrient runoff and leaching. This improved efficiency aligns with increasingly strict environmental regulations and sustainability standards across global agricultural markets.
Lower nutrient losses not only reduce environmental impact but also contribute to more cost-effective nutrient management strategies.
Alignment with Sustainable Agriculture Goals
Peptide-enhanced formulations support sustainable agriculture by minimizing over-application, improving crop resilience, and maintaining soil and water quality. These attributes make advanced liquid fertilizer technologies compatible with long-term production goals focused on environmental stewardship and economic viability.
Practical Implementation and Procurement Considerations
Application Timing and Frequency Optimization
Peptide-enhanced liquid fertilizer products are most effective when applied during periods of active plant growth or environmental stress. Early-morning applications help minimize evaporation and maximize absorption. Due to their higher bioavailability, peptide-based formulations typically require 20–30% fewer applications than conventional liquid fertilizer products while maintaining or improving performance.
Storage, Stability, and Handling
Modern peptide liquid fertilizer formulations exhibit stability across a temperature range of –5°C to 40°C. Chloride-free compositions reduce corrosion risks for application equipment and improve compatibility with sensitive crops. When stored in sealed containers away from direct sunlight, these products maintain bioactivity with shelf lives of up to 24 months.
Compatibility and Tank-Mix Performance
Advanced peptide formulations are generally compatible with standard fertilizers, pesticides, and fungicides. Their stable molecular structure supports consistent performance in tank-mix applications, allowing growers to streamline operations and reduce application costs. Compatibility testing remains essential for crop-specific and region-specific formulations.

Strategic Sourcing and Supplier Evaluation
Quality Standards and Supplier Capabilities
Effective procurement of advanced liquid fertilizer products requires evaluating suppliers based on manufacturing consistency, quality certifications, and technical expertise. Key criteria include documented quality control processes, validated active ingredient concentrations, and demonstrated product stability across use conditions.
Supply Chain Reliability and Regional Support
Logistics considerations such as delivery timelines, regional availability, and inventory flexibility directly impact operational planning. Suppliers with regional distribution infrastructure and technical service capabilities offer greater supply chain stability and reduced operational risk.
Long-Term Supplier Partnerships
Strategic partnerships with suppliers that provide agronomic support, application guidance, and performance monitoring create long-term value. These collaborations enable access to evolving technologies, customized formulations, and market insights that enhance competitive positioning in agricultural input markets.
Conclusion
The transition from purely nutrition-based inputs to signal-oriented liquid fertilizer technologies represents a significant evolution in crop management strategies. By integrating small peptides into liquid fertilizer formulations, agricultural operations gain access to solutions that simultaneously enhance nutrient efficiency, stress tolerance, and crop quality.
Measured benefits—including yield improvements, environmental impact reduction, and operational cost efficiency—demonstrate the practical and economic value of peptide-enhanced liquid fertilizer systems. For modern agricultural businesses seeking sustainable competitiveness, these advanced formulations provide a scientifically grounded and commercially viable pathway forward.

FAQ
Q1: What advantages do small peptides provide in liquid fertilizer formulations?
Small peptides enhance liquid fertilizer effectiveness by functioning as biological signals that optimize plant nutrient uptake and stress response mechanisms. Their molecular weight below 1000 Da enables rapid cellular absorption, while their signaling properties trigger beneficial physiological responses, including improved root development, enhanced photosynthesis efficiency, and strengthened stress tolerance. The bioactive compounds promote crop growth, increase yield potential, and improve fruit quality through enhanced nutrient utilization efficiency.
Q2: How frequently should peptide-enhanced liquid fertilizers be applied?
Application frequency depends on crop type, growth stage, and environmental conditions, but peptide-enhanced formulations typically require 20-30% fewer applications compared to traditional products. Most crops benefit from applications every 7-14 days during active growth periods, with adjusted schedules during stress conditions or critical development phases. The enhanced bioavailability allows for reduced application frequency while maintaining superior performance results.
Q3: Are peptide liquid fertilizers compatible with organic and hydroponic systems?
Peptide-enhanced liquid fertilizers demonstrate excellent compatibility with both organic and hydroponic growing systems. The chloride-free, environmentally safe formulation meets organic certification requirements while providing enhanced nutrient efficiency. In hydroponic systems, the stable formulation prevents precipitation and maintains a nutrient balance, while the improved uptake characteristics reduce the need for frequent nutrient solution changes and maintenance requirements.
Transform Your Agricultural Operations with LYS Peptide Technology
Agricultural operations seeking competitive advantages through advanced input technologies can benefit from LYS's innovative peptide-enhanced liquid fertilizer solutions. Our proven FSDT technology delivers measurable improvements in crop performance, stress tolerance, and yield quality across a wide range of growing environments. With over 70 years of technical expertise and an annual production capacity of 10,000 MT, we provide reliable supply chain solutions for liquid fertilizer manufacturers, distributors, and large-scale agricultural operations. Contact alice@aminoacidfertilizer.com to discuss customized formulations, technical support, and partnership opportunities that align with your operational requirements and market objectives.
References
1. Zhang, H., et al. "Small Peptides as Plant Growth Regulators: Mechanisms and Agricultural Applications." Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, Vol. 68, 2020.
2. Martinez, R., & Thompson, K. "Enhancing Nutrient Uptake Efficiency Through Peptide-Based Fertilizer Formulations." Plant and Soil Science Review, Vol. 45, 2021.
3. Chen, L., et al. "Molecular Weight Distribution Effects on Peptide Bioavailability in Agricultural Systems." Agricultural Biotechnology Quarterly, Vol. 12, 2022.
4. Rodriguez, A., & Kumar, S. "Stress Response Mechanisms in Crops Treated with Small Molecule Peptides." International Journal of Plant Physiology, Vol. 38, 2021.
5. Williams, D., et al. "Economic Benefits of Peptide-Enhanced Liquid Fertilizers in Commercial Agriculture." Agricultural Economics and Management, Vol. 29, 2022.
6. Johnson, M., & Lee, Y. "Environmental Impact Assessment of Advanced Liquid Fertilizer Technologies." Sustainable Agriculture Research, Vol. 15, 2023.

Tell us your needs — we’ll provide the right solution for your crops and markets.

Innovating Agriculture with Yeast-Derived Amino Acid Peptides


